Warts
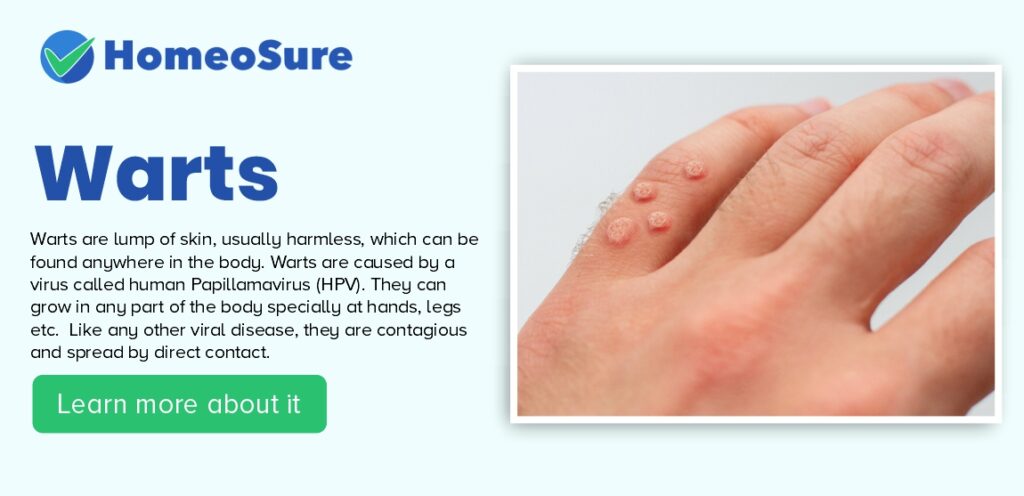
Warts are lump of skin, usually harmless, which can be found anywhere in the body. Warts are caused by a virus called human Papillamavirus (HPV). They can grow in any part of the body specially at hands, legs etc. Like any other viral disease, they are contagious and spread by direct contact.
I can confidently say homeopathic treatment is perhaps the most effective treatment that significantly reduces the tendency for recurrence. If detected earlier it can be treated easily without any side effects. Now, Let us understand what are the symptoms of warts to detect them at early stages and later on to understand how to remove warts:
SYMPTOMS OF WARTS
- Abnormal growths on skin which are usually painless
- Some of the warts contain tiny blood vessels, they appear to be as small as small seeds with black dots.
- Grow in clusters – Easily can be detected.
- Word of caution: In females, sometimes they appear near private parts to make you vulnerable to cancer of cervix
How to Remove Warts by Homeopathic Treatment
Homeopathy offers the most permanent treatment for this stubborn & recurrent condition. It helps prevent the occurrence of warts by improving the “immunity” or “disease resisting capacity” of the individual.
Homeopathic treatment given correctly helps prevent the spread of infection as well as its complications. Appropriate homeopathic treatment for warts can eliminate the tendency of formation of warts as well as help avoid recurrences.
Homeopathic treatment is targeted towards UPROOTING THE DISEASE and ensuring health with no side effects. For prescribing to an individual, a PLAN OF TREATMENT is followed which involves:
- Getting through understanding the case which includes complete case taking (analyzing patient as an individual) along with patient history and family history
- Diagnosis of patient and disease
- Individual assessment of the case
- Prescribing the most suitable individual constitutional remedy