Eczema
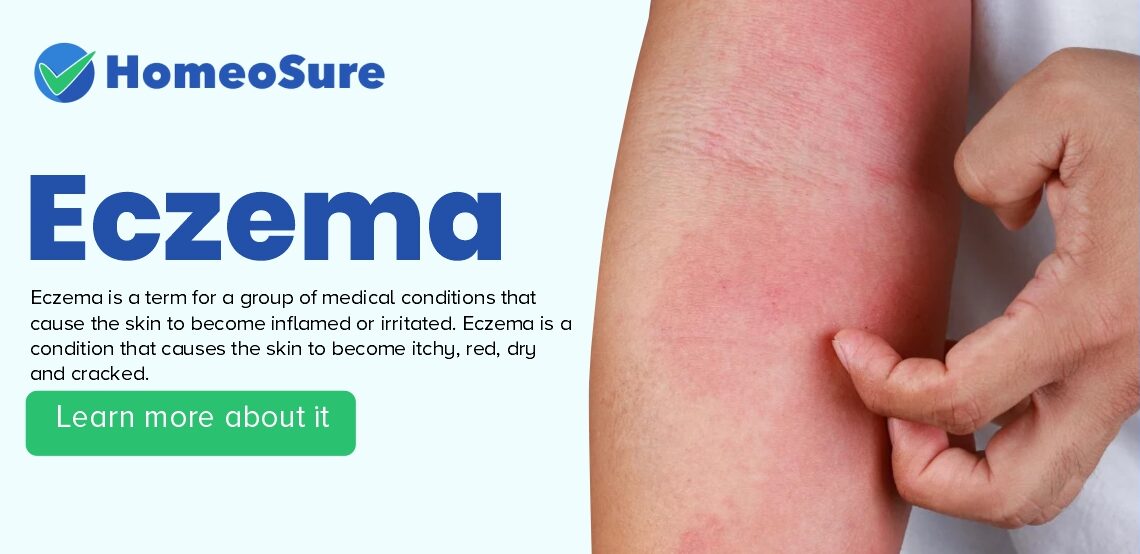
Eczema is a term for a group of medical conditions that cause the skin to become inflamed or irritated. Eczema is a condition that causes the skin to become itchy, red, dry and cracked. It is a long-term (chronic) condition in most people, although it can improve over time, especially in children.
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin. Types of eczema include:
- Atopic Dermatitis – most common form
- Discoid – a type of eczema that occurs in circular or oval patches on the skin
- Contact dermatitis – a type of eczema that occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance
- Varicose – a type of eczema that most often affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
- Seborrhoeic – a type of eczema where red, scaly patches develop on the sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears and scalp
- Dyshidrotic (pompholyx) – a type of eczema that causes tiny blisters to erupt across the palms of the hands
CAUSES OF ECZEMA
The exact cause of disease is unknown, but it’s thought to be linked to an overactive response by the body’s immune system to an irritant. It is this response that causes the symptoms of eczema
There are two groups of eczema’s on the basis of etiology:
- Exogenous eczema is mostly caused by contact with external factors such as irritant substances, certain allergens and due to photo sensitivity
- Endogenous eczema is due to internal factors such as a generalized and prolonged hypersensitivity (atopy) to certain environmental factors. These factors could be chemicals, drugs, pollen, dust-mites, etc. These individuals also frequently exhibit one or more of other disorders such as asthma, hay fever, urticaria, food allergies, etc.
SYMPTOMS OF ECZEMA
- Dryness of skin
- Recurrent skin rashes with itching usually more in the night
- Swelling, inflammation, crusting, flaking or blistering of skin
- Papules and vesicles may also be present
COMPLICATIONS
Eczema can lead to:
- Lichenification: In chronic cases, the skin becomes thick, leathery and high-colored as a result of the constant irritation and itching.
- Infections: Skin can break up and cause open wounds leading to the possibility of bacterial infections
- Eye Complications: Disease around the eye can cause permanent damage to the cornea because of constant itching and inflammation of lids
- Exfoliative: This involves oozing and crusting all over the skin with fever, leading to toxicity and generalized water loss
- Other: Lack of proper sleep and psychological disturbances may occur because of the embarrassment and stress of appearance
PREVENTIVE MEASURES
Eczema outbreaks can sometimes be avoided or the severity lessened by following these simple tips:
- Moisturize frequently
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature or humidity
- Avoid sweating or overheating
- Reduce stress
- Avoid scratchy materials, such as wool
- Avoid harsh soaps, detergents, and solvents
- Be aware of any foods that may cause an outbreak and avoid those foods
HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENT
Homeopathy, today, is the most effective treatment for Eczema. It works towards balancing the susceptibility of the individual by prescribing a remedy which is most suitable to his or her constitution.
Homeopathic treatment is targeted towards UPROOTING THE DISEASE and ensuring health with no side effects. For prescribing to an individual, a PLAN OF TREATMENT is followed which involves:
- GETTING THOROUGH UNDERSTANDING OF CASE which includes complete case taking (analyzing patient as an individual) along with patient history and family history
- DIAGNOSIS OF PATIENT AND DISEASE
- INDIVIDUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE CASE
- PRESCRIBING THE MOST SUITABLE INDIVIDUAL CONSTITUTIONAL REMEDY